Mapping the Nexus of Urban Water Crisis, Social Capital, and Social Determinants of Health: A Bibliometric Analysis
A Review of Research Trends, Intellectual Structure, and Future Directions
DOI:
https://doi.org/10.1000/1wghcz54کلمات کلیدی:
Urban Resilience, Climate Change, Social Capital, Urban Water Crisis, Bibliometric Analysisچکیده
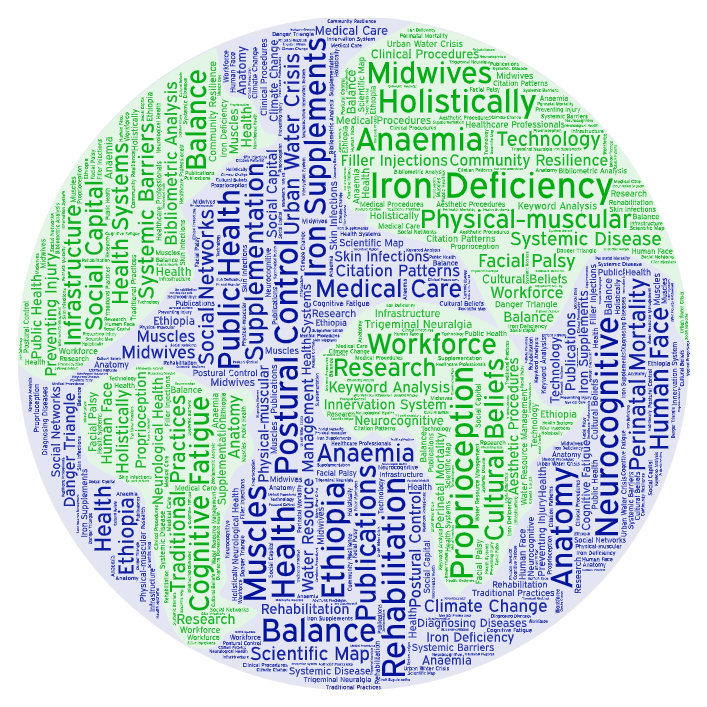
ABSTRACT. Urban water crisis is one of the major problems of the twenty-first century, which is worsened by climate change. Social capital is a key element in community resilience. This study will perform a bibliometric analysis and produce a scientific map of the field. This study uses a bibliometric analysis of a number of relevant scientific publications. We looked at metrics like yearly scientific output, citation patterns, keyword co-occurrence analysis, and author impact. The results indicate a significant surge in publications starting around 2020, reaching a peak of 20 articles in 2024. Research from those years had a significant impact, as evidenced by a notable citation surge in 2005 with over 120 citations and a secondary, notable peak in 2023 with over 80 citations. The Core Crisis (water, climate, risk), The Urban and Geographic Context (city, urban), The Social Dimensions and Impacts (social, capital, policy), and The Research Approach (case study, impact) were the four primary clusters found by keyword analysis. Writers like L. and S. Blancafort. He was determined to be the most influential researcher. Urban water crisis and social capital research is a multidisciplinary and expanding field. Understanding the function of social networks in sustainable water resource management is an area of growing research interest. Future developments should focus on integrating social tactics with advances in infrastructure and technology. © 2025 Published by Public Knowledge Project (PKP).
دانلودها

دانلود
چاپ شده
شماره
نوع مقاله
مجوز
حق نشر 2025 Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License

این پروژه تحت مجوز بین المللی Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives 4.0 می باشد.
This open-access journal is published under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License which permits Share (copy and redistribute the material in any medium or format) and Adapt (remix, transform, and build upon the material) under the Attribution-NonCommercial term